Introduction
This is the 18th post in the series Elegant Data Visualization with ggplot2.
In the previous post, we learnt how to modify the legend of plot when alpha
is mapped to a categorical variable. In this post, we will learn to modify legend
- title
- label
- and bar
So far, we have learnt to modify the components of a legend using scale_*
family of functions. Now, we will use the guide argument and supply it
values using the guide_legend() function.
Libraries, Code & Data
We will use the following libraries in this post:
All the data sets used in this post can be found here and code can be downloaded from here.
Title
Title Alignment
The horizontal alignment of the title can be managed using the title.hjust
argument. It can take any value between 0 and 1.
- 0 (left)
- 1 (right)
In the below example, we align the title to the center by assigning the value
0.5.
ggplot(mtcars) + geom_point(aes(disp, mpg, color = factor(cyl))) +
scale_color_manual(values = c("red", "blue", "green"),
guide = guide_legend(title = "Cylinders", title.hjust = 0.5))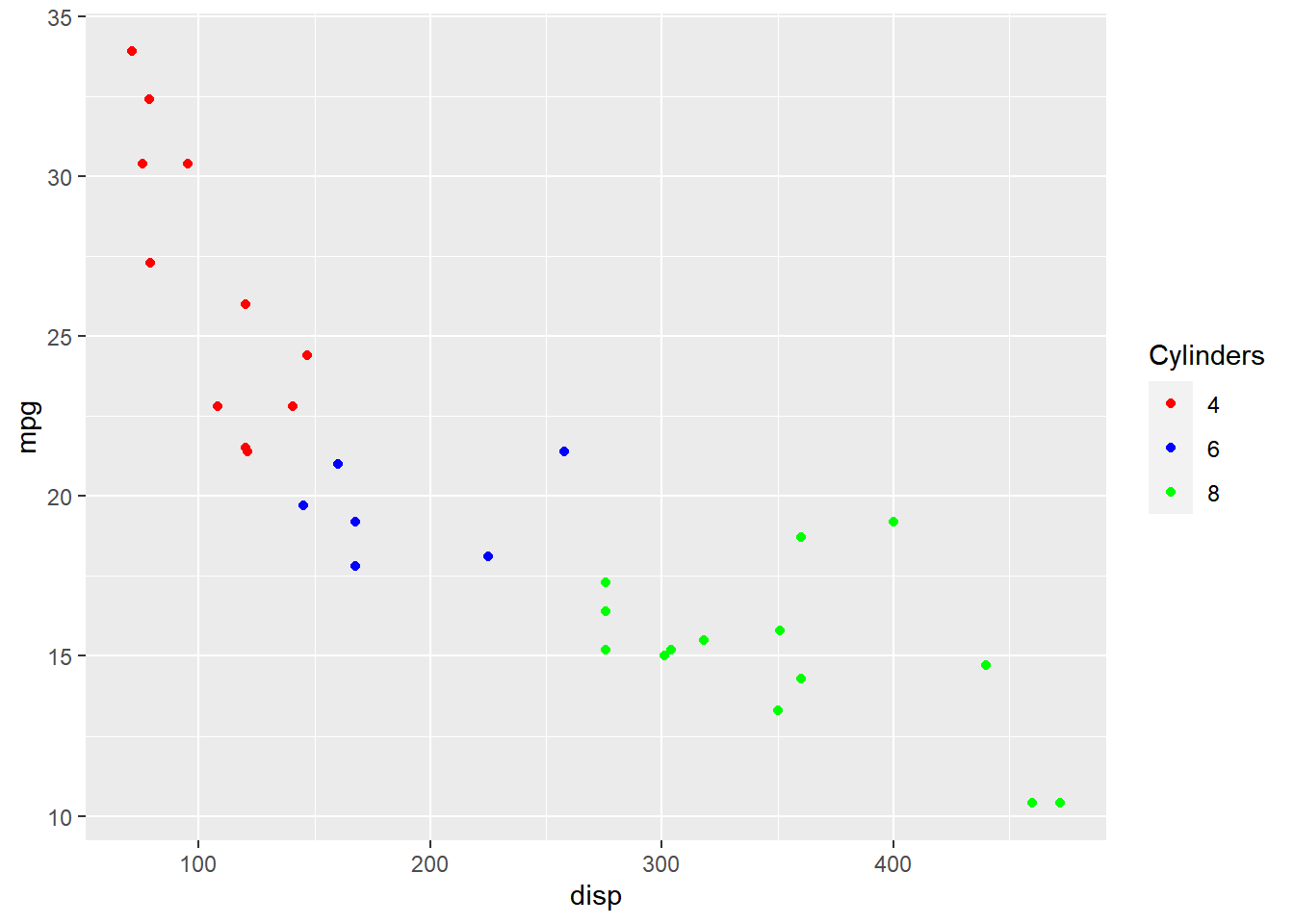
Title Alignment (Vertical)
To manage the vertical alignment of the title, use title.vjust.
ggplot(mtcars) + geom_point(aes(disp, mpg, color = hp)) +
scale_color_continuous(guide = guide_colorbar(
title = "Horsepower", title.position = "top", title.vjust = 1))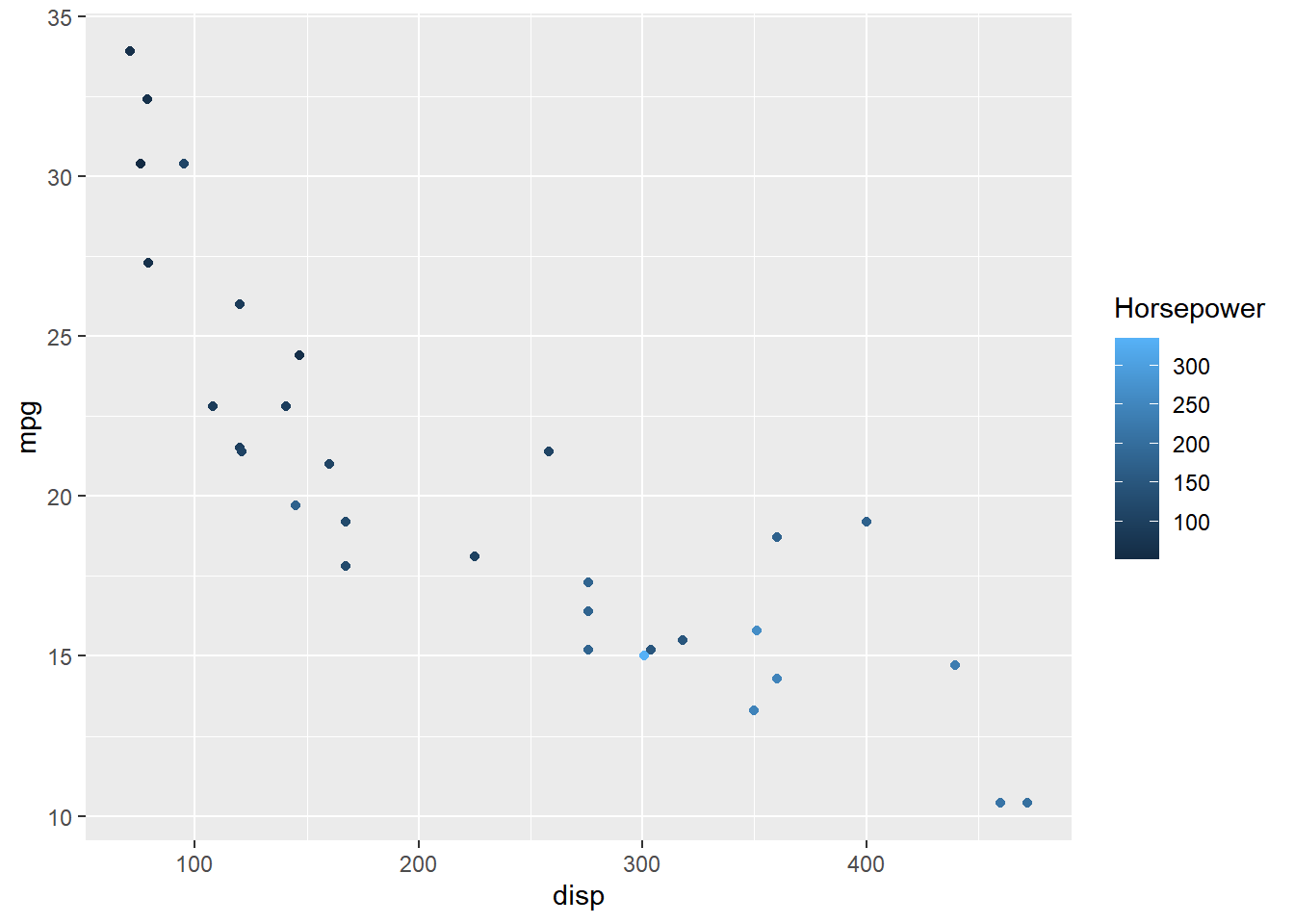
Title Position
The position of the title can be managed using title.posiiton argument. It
can be positioned at:
- top
- bottom
- left
- right
ggplot(mtcars) + geom_point(aes(disp, mpg, color = factor(cyl))) +
scale_color_manual(values = c("red", "blue", "green"),
guide = guide_legend(title = "Cylinders", title.hjust = 0.5,
title.position = "top"))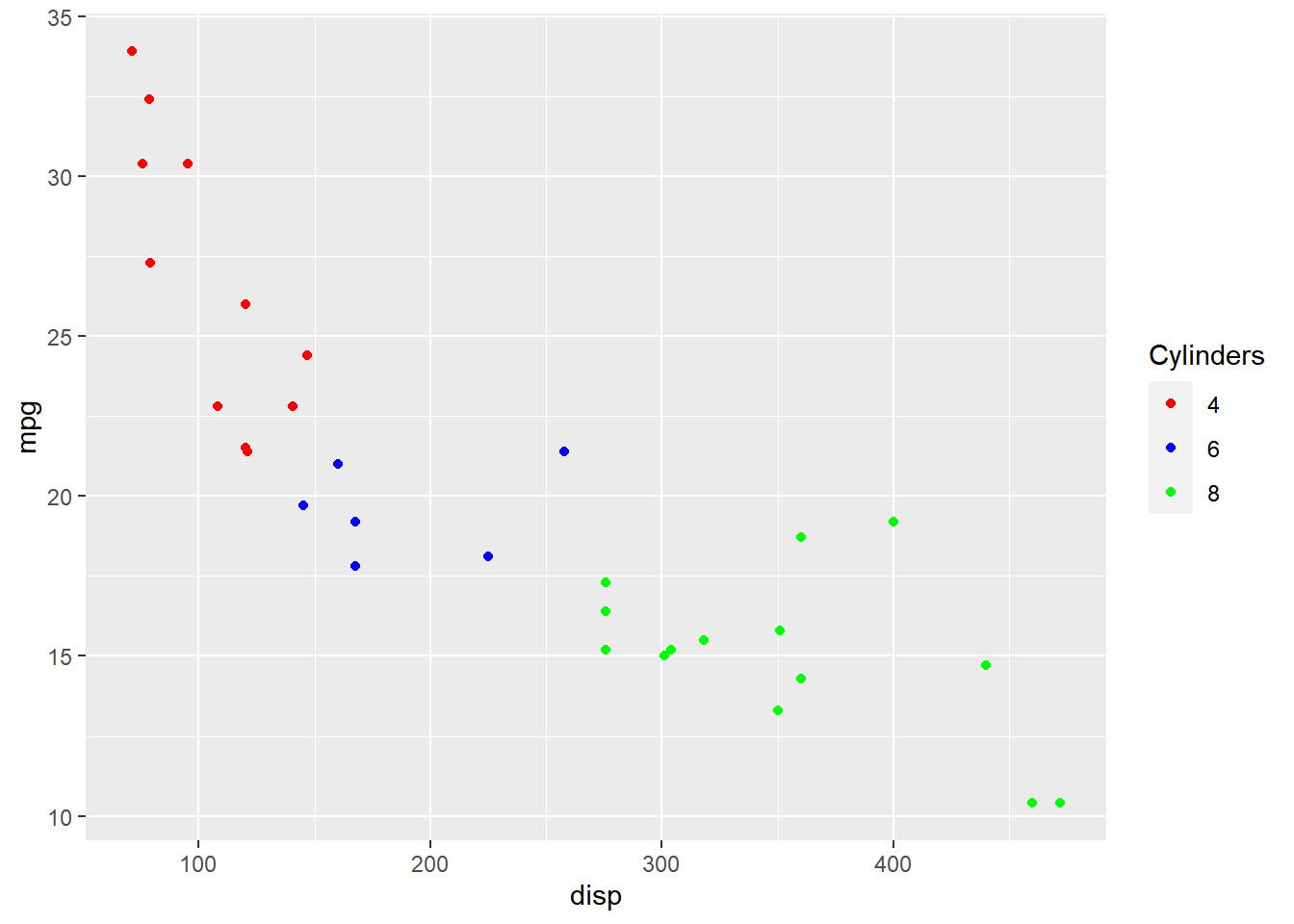
Label
Label Position
The position of the label can be managed using the label.position argument.
It can be positioned at:
- top
- bottom
- left
- right
In the below example, we position the label at right.
ggplot(mtcars) + geom_point(aes(disp, mpg, color = factor(cyl))) +
scale_color_manual(values = c("red", "blue", "green"),
guide = guide_legend(label.position = "right"))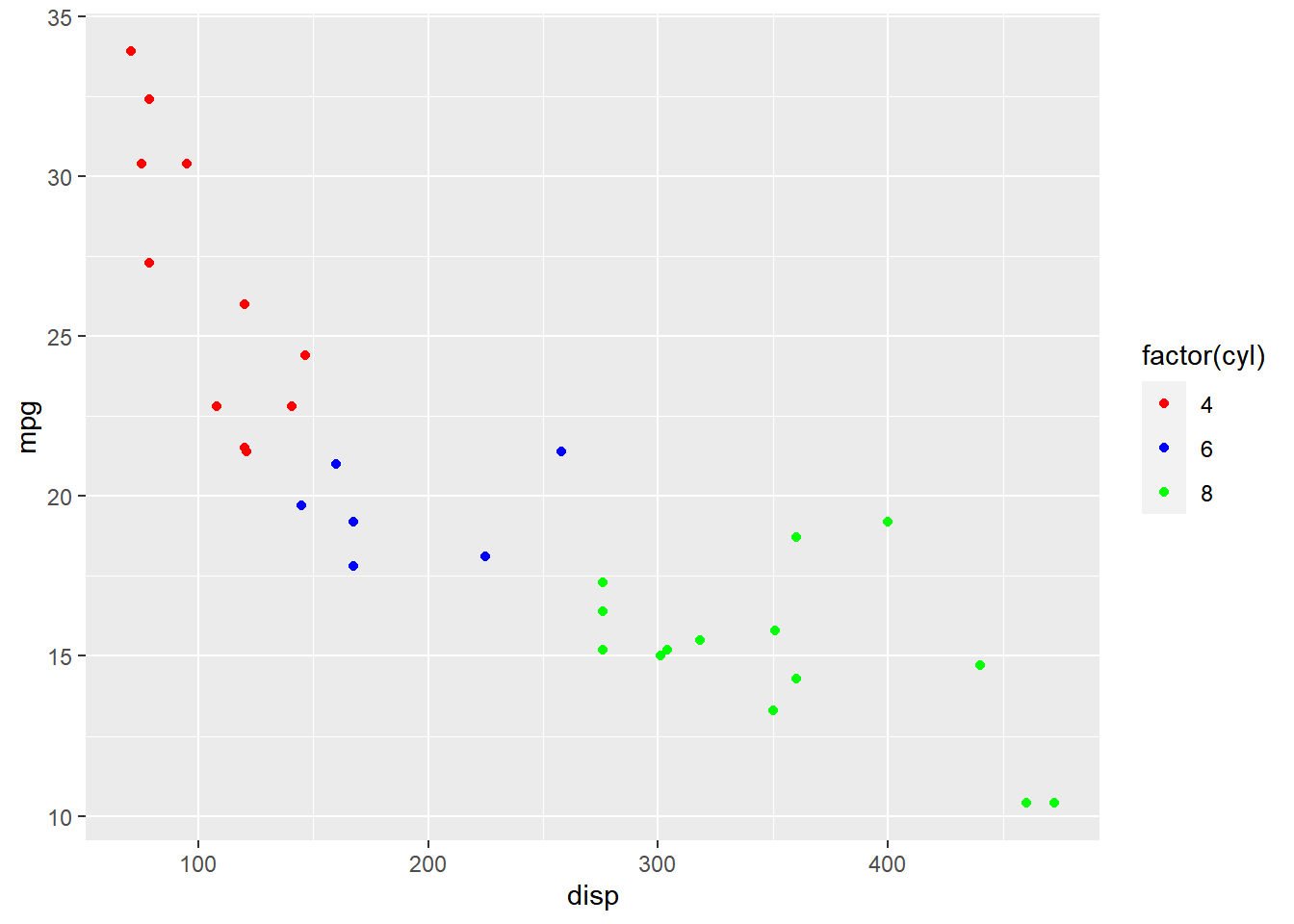
Label Alignment
The horizontal alignment of the label can be managed using the label.hjust
argument. It can take any value between 0 and 1.
- 0 (left)
- 1 (right)
In the below example, we align the label to the center by assigning the value
0.5.
- alignment
- 0 (left)
- 1 (right)
ggplot(mtcars) + geom_point(aes(disp, mpg, color = factor(cyl))) +
scale_color_manual(values = c("red", "blue", "green"),
guide = guide_legend(label.hjust = 0.5))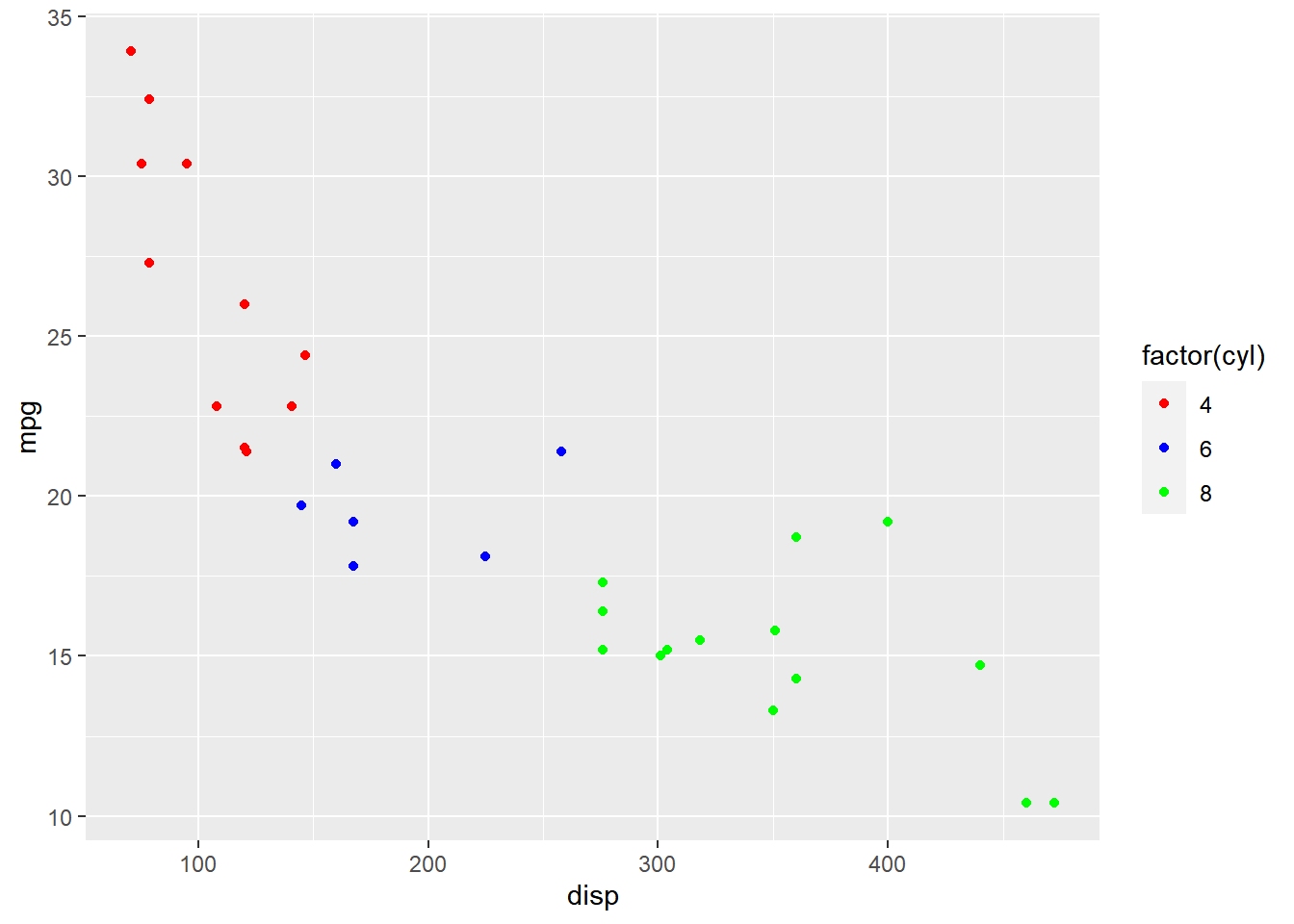
Labels Alignment (Vertical)
The vertical alignment of the label can be managed using the label.vjust
argument.
ggplot(mtcars) +
geom_point(aes(disp, mpg, color = hp)) +
scale_color_continuous(guide = guide_colorbar(
label.vjust = 0.8))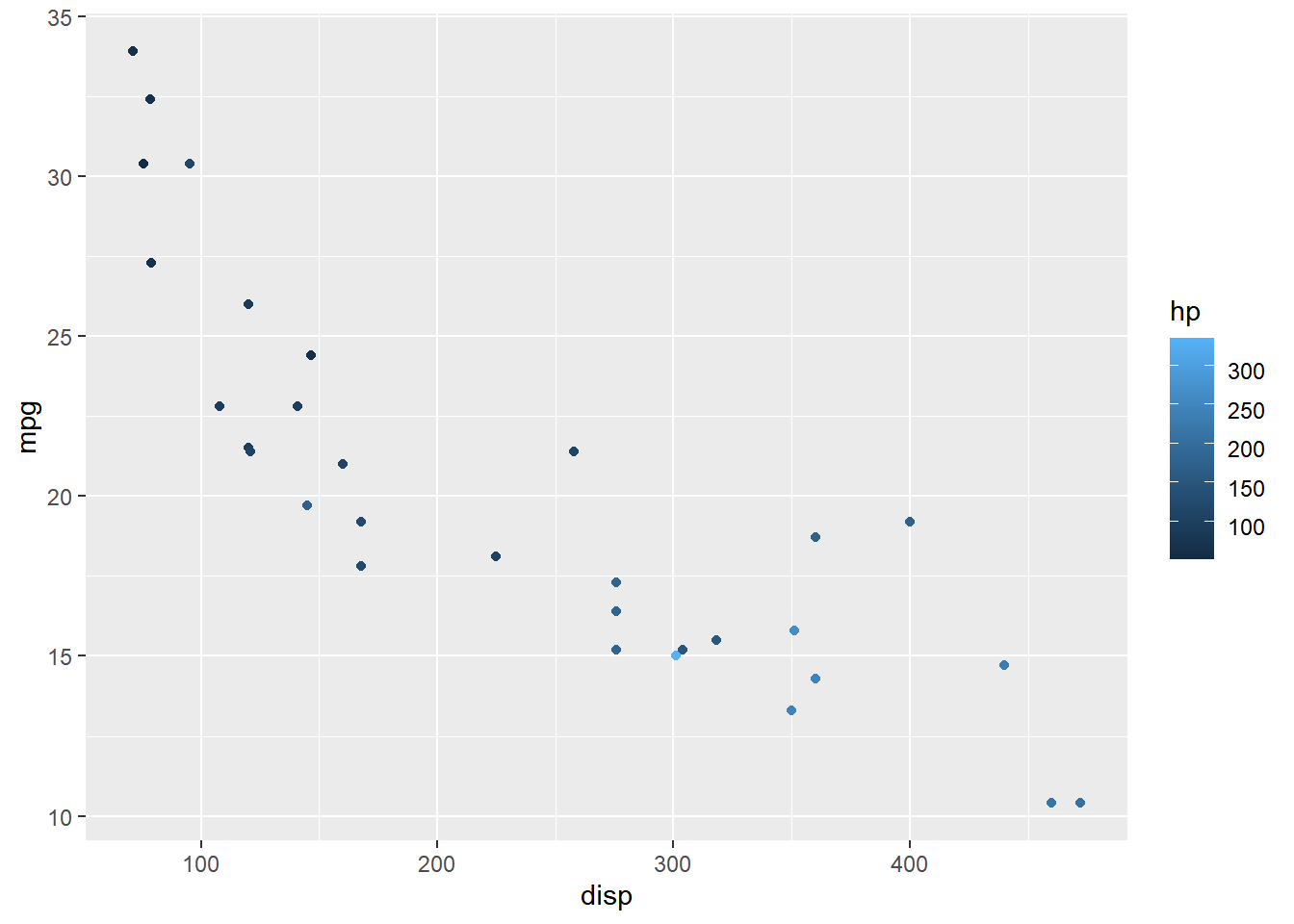
Direction
The direction of the label can be either horizontal or veritcal and it can be
set using the direction argument.
ggplot(mtcars) + geom_point(aes(disp, mpg, color = factor(cyl))) +
scale_color_manual(values = c("red", "blue", "green"),
guide = guide_legend(direction = "horizontal"))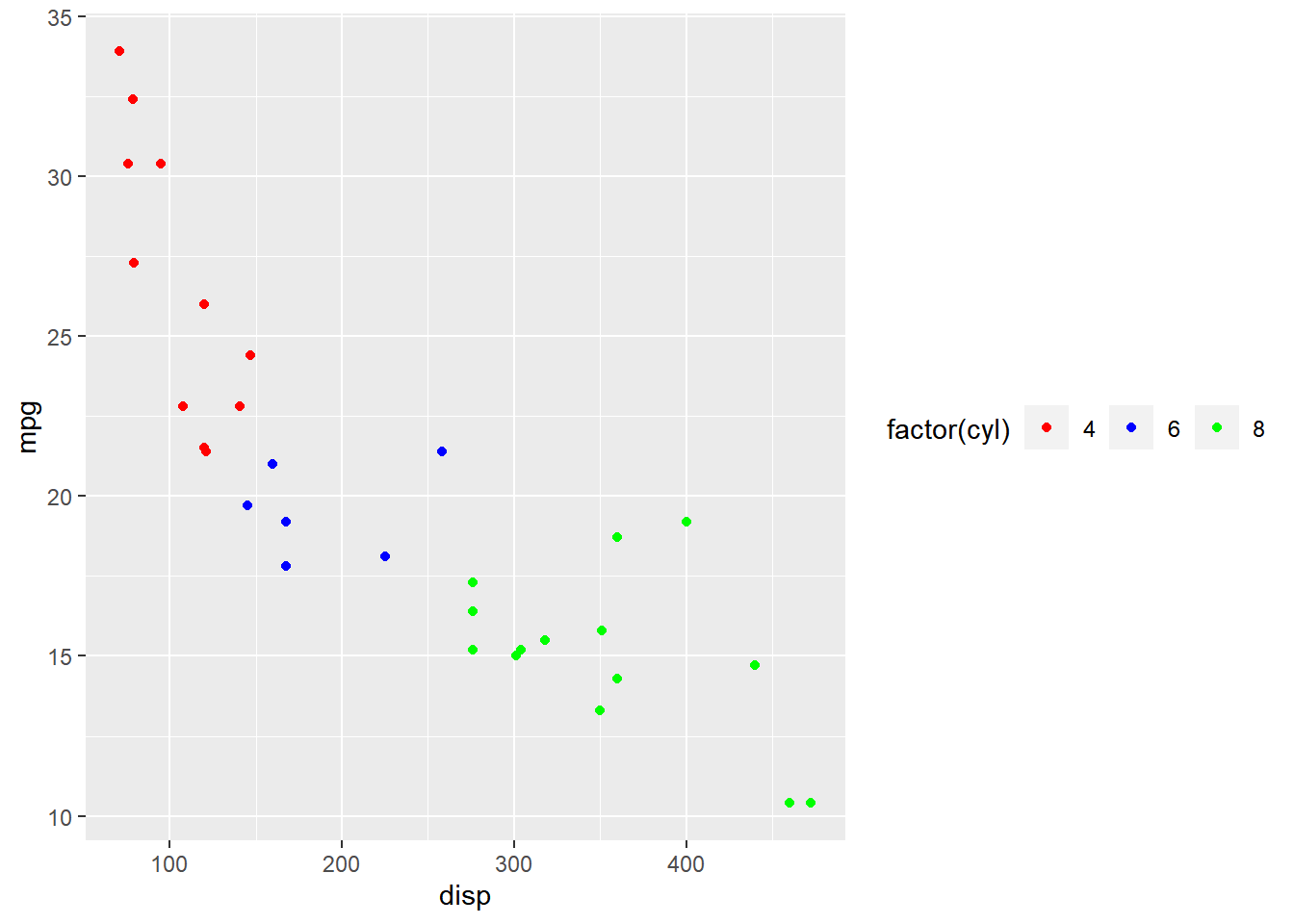
Rows
The label can be spread across multiple rows using the nrow argument. In the
below example, the label is spread across 2 rows.
ggplot(mtcars) + geom_point(aes(disp, mpg, color = factor(cyl))) +
scale_color_manual(values = c("red", "blue", "green"),
guide = guide_legend(nrow = 2))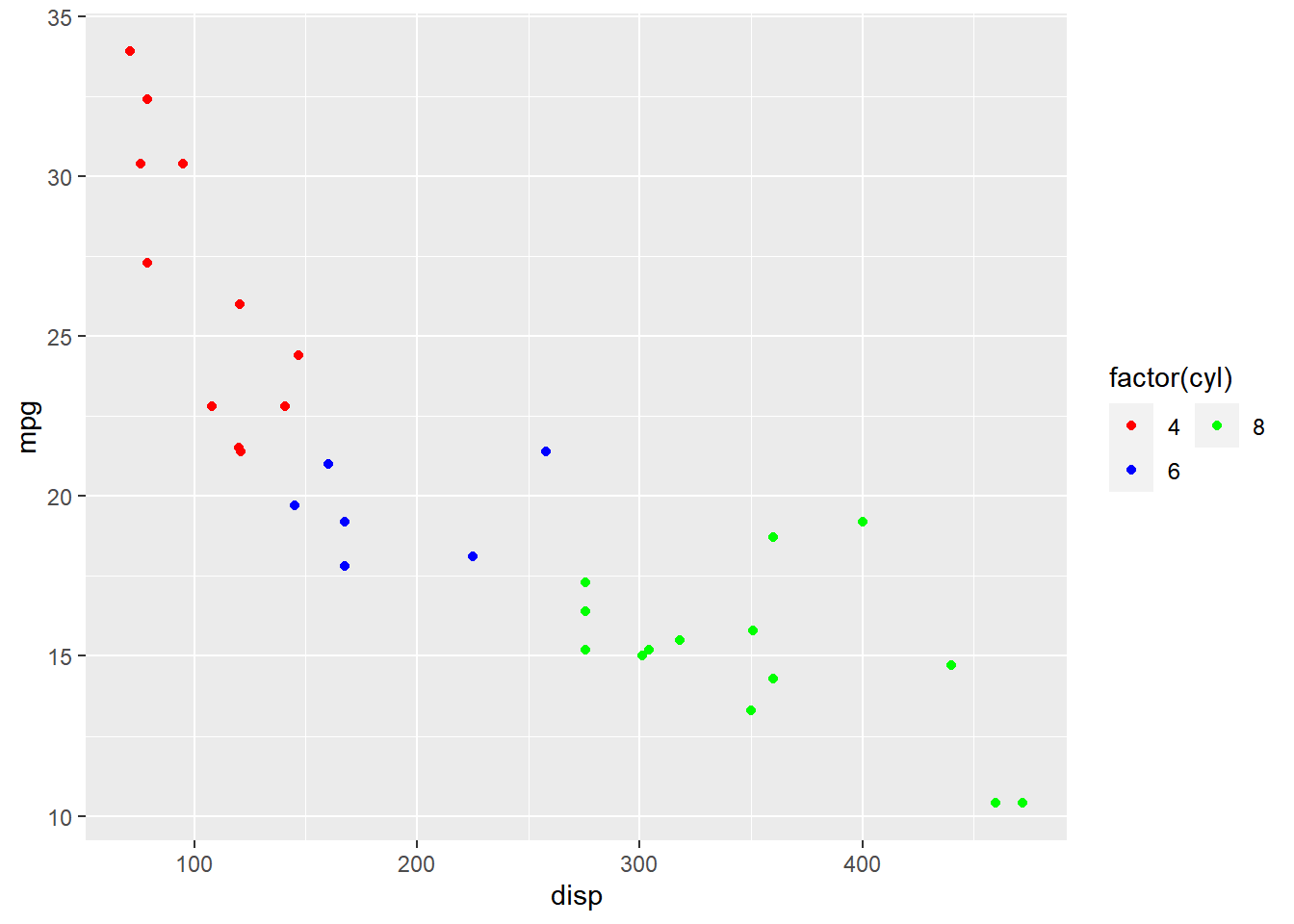
Reverse
The order of the labels can be reversed using the reverse argument. We need
to supply logical values i.e. either TRUE or FALSE. If TRUE, the order
will be reversed.
ggplot(mtcars) + geom_point(aes(disp, mpg, color = factor(cyl))) +
scale_color_manual(values = c("red", "blue", "green"),
guide = guide_legend(reverse = TRUE))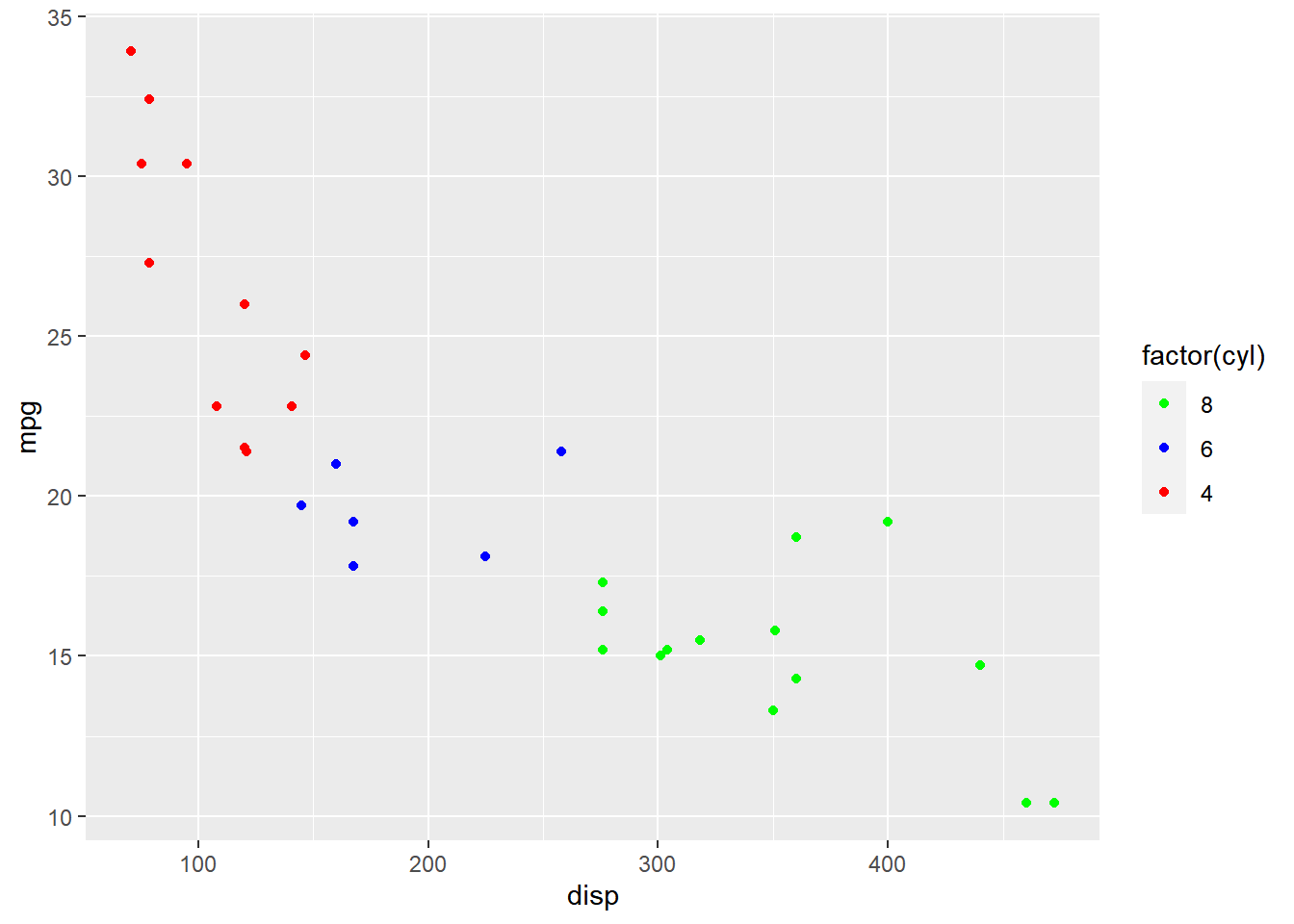
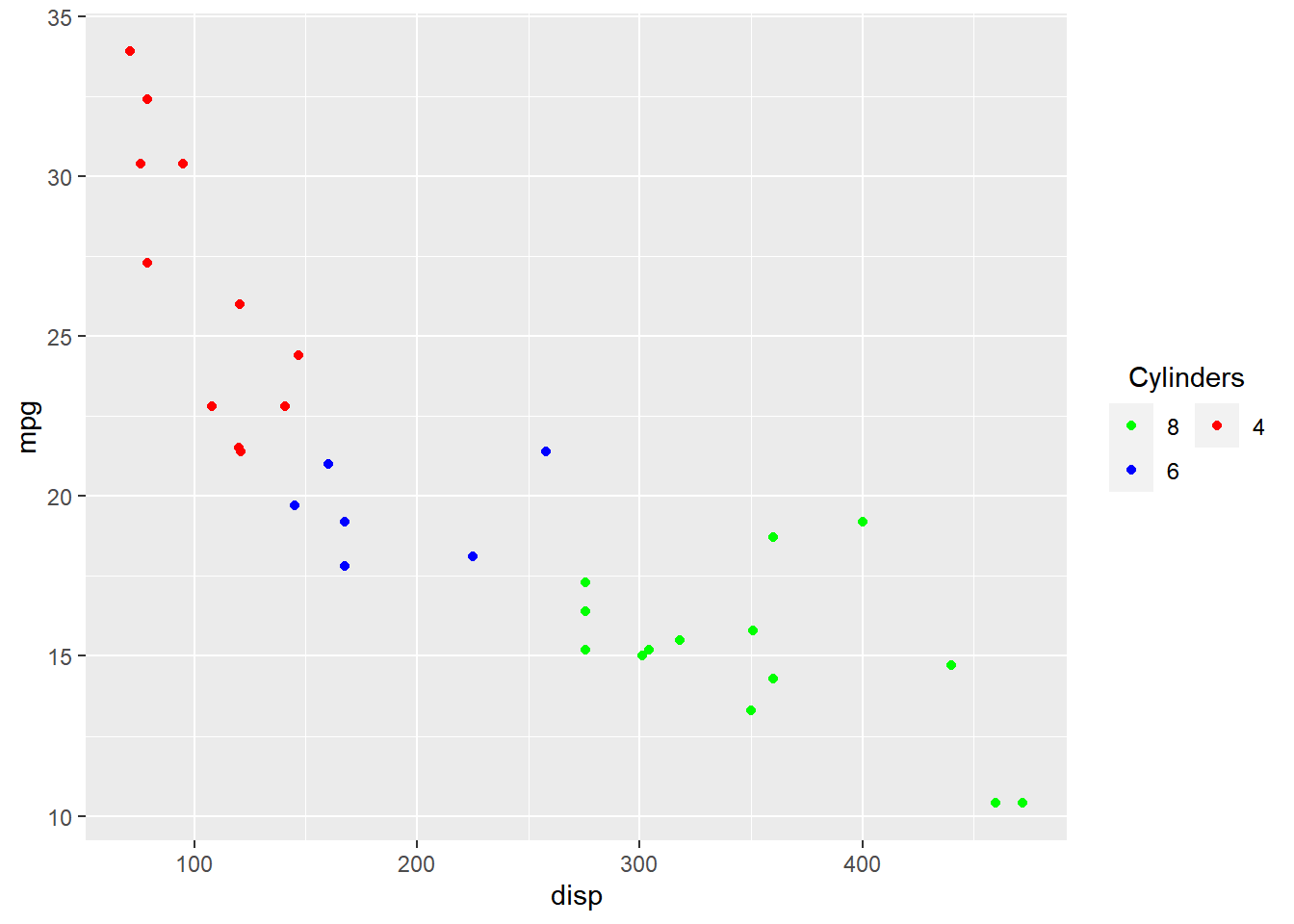
Putting it all together…
ggplot(mtcars) + geom_point(aes(disp, mpg, color = factor(cyl))) +
scale_color_manual(values = c("red", "blue", "green"),
guide = guide_legend(title = "Cylinders", title.hjust = 0.5,
title.position = "top", label.position = "right",
direction = "horizontal", label.hjust = 0.5, nrow = 2, reverse = TRUE)
)
Legend Bar
So far we have looked at modifying components of the legend when it acts as a
guide for color, fill or shape i.e. when the aesthetics have been mapped
to a categorical variable. In this section, you will learn about
guide_colorbar() which will allow us to modify the legend when the aesthetics
are mapped to a continuous variable.
Plot
Let us start with a scatter plot examining the relationship between displacement
and miles per gallon from the mtcars data set. We will map the color of the points
to the hp variable.
ggplot(mtcars) +
geom_point(aes(disp, mpg, color = hp))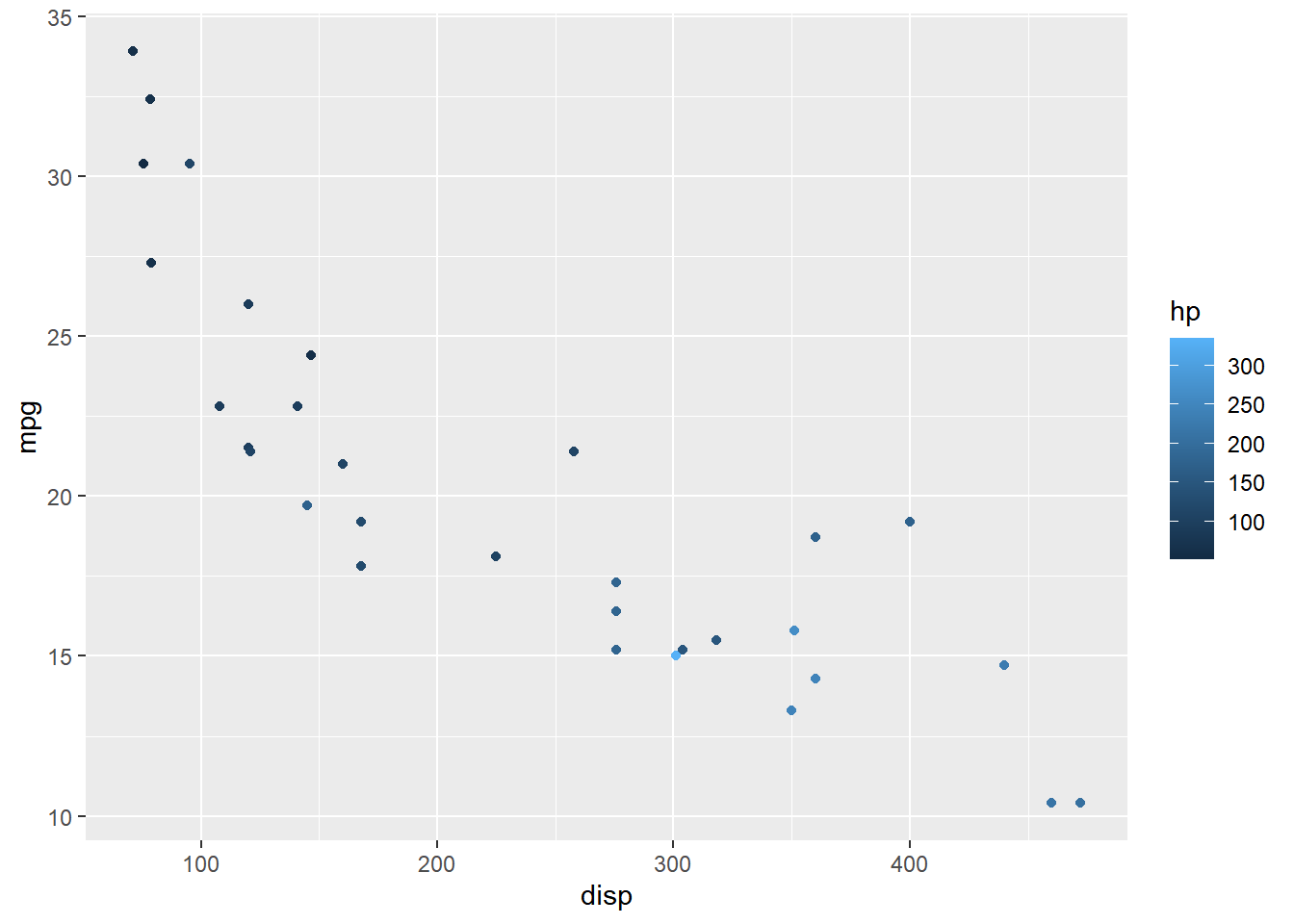
Width
The width of the bar can be modified using the barwidth argument. It is used
inside the guide_colorbar() function which itself is supplied to the guide
argument of scale_color_continuous().
ggplot(mtcars) +
geom_point(aes(disp, mpg, color = hp)) +
scale_color_continuous(guide = guide_colorbar(
barwidth = 10))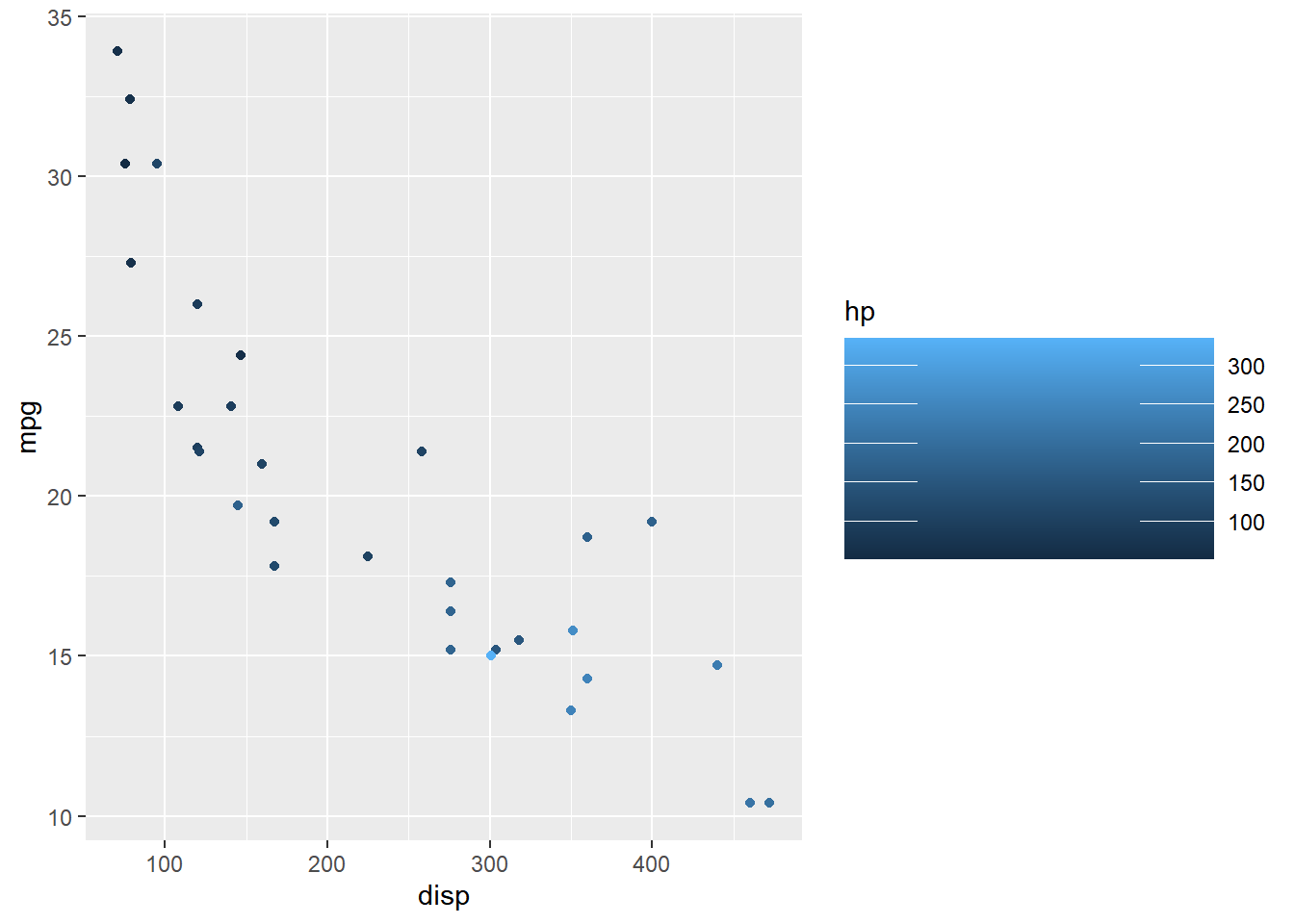
Height
Similarly, the height of the bar can be modified using the barheight argument.
ggplot(mtcars) +
geom_point(aes(disp, mpg, color = hp)) +
scale_color_continuous(guide = guide_colorbar(
barheight = 3))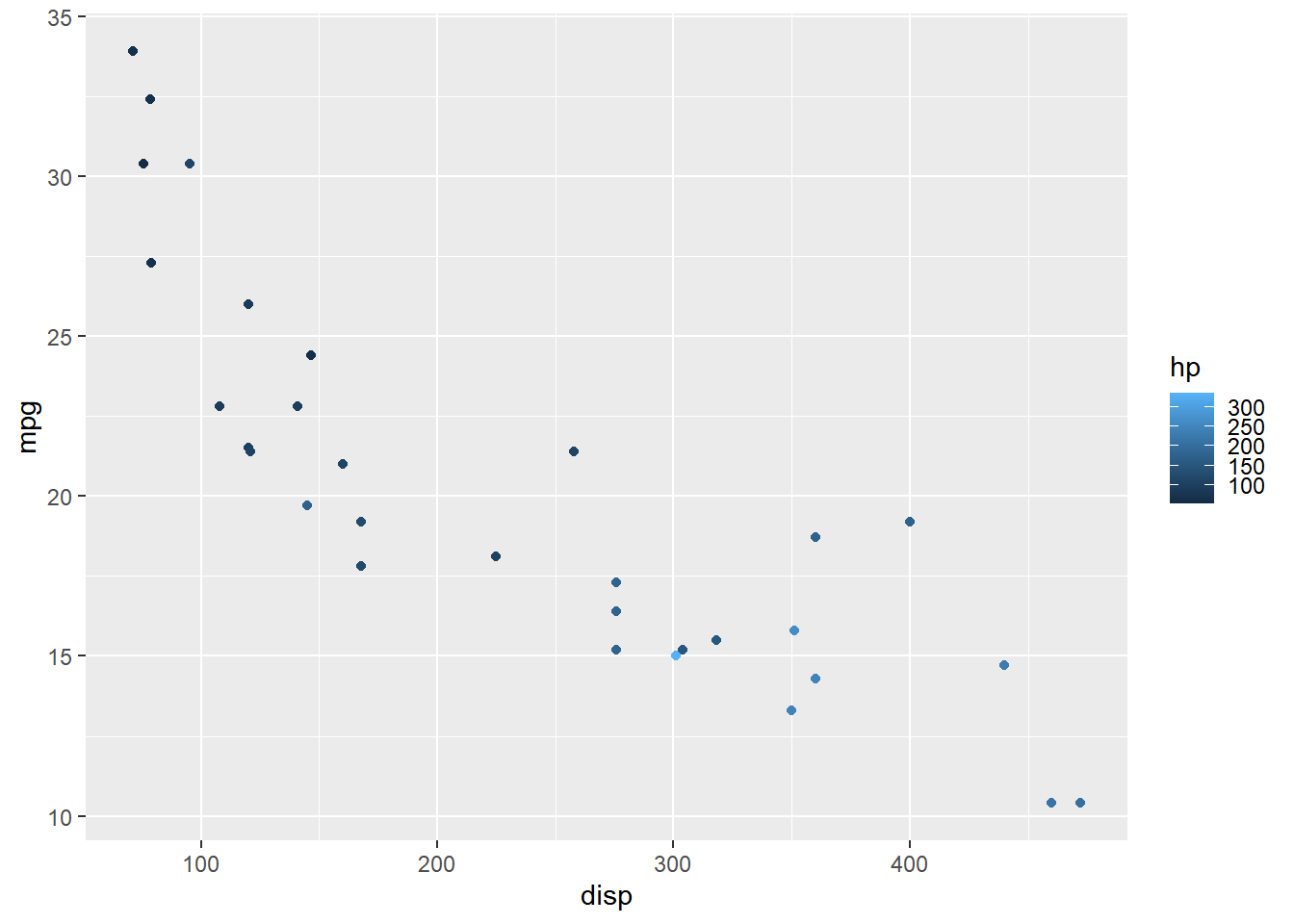
Bins
The nbin argument allows us to specify the number of bins in the bar.
ggplot(mtcars) +
geom_point(aes(disp, mpg, color = hp)) +
scale_color_continuous(guide = guide_colorbar(
nbin = 4))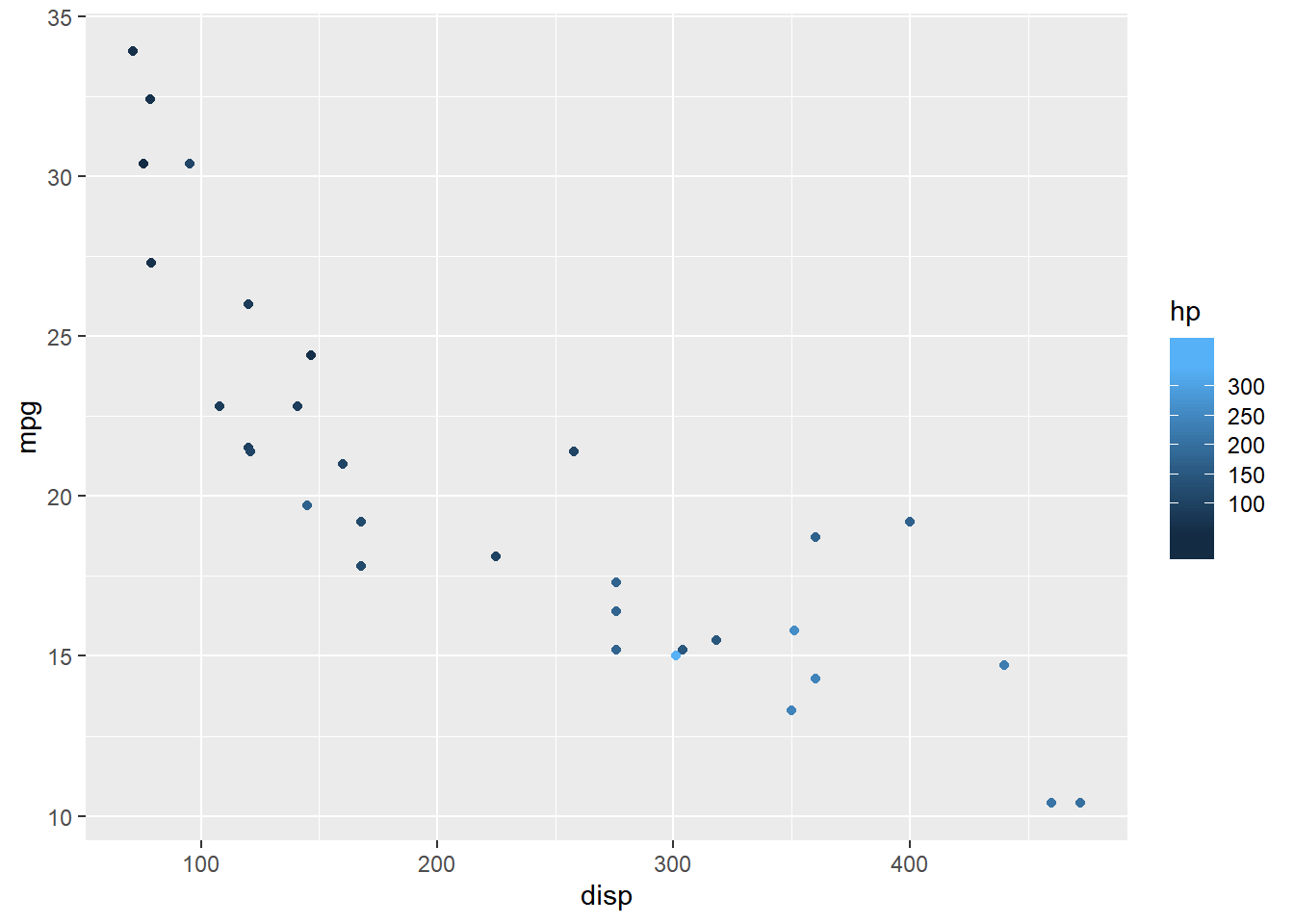
Ticks
The ticks of the bar can be removed using the ticks argument and setting it
to FALSE.
ggplot(mtcars) +
geom_point(aes(disp, mpg, color = hp)) +
scale_color_continuous(guide = guide_colorbar(
ticks = FALSE))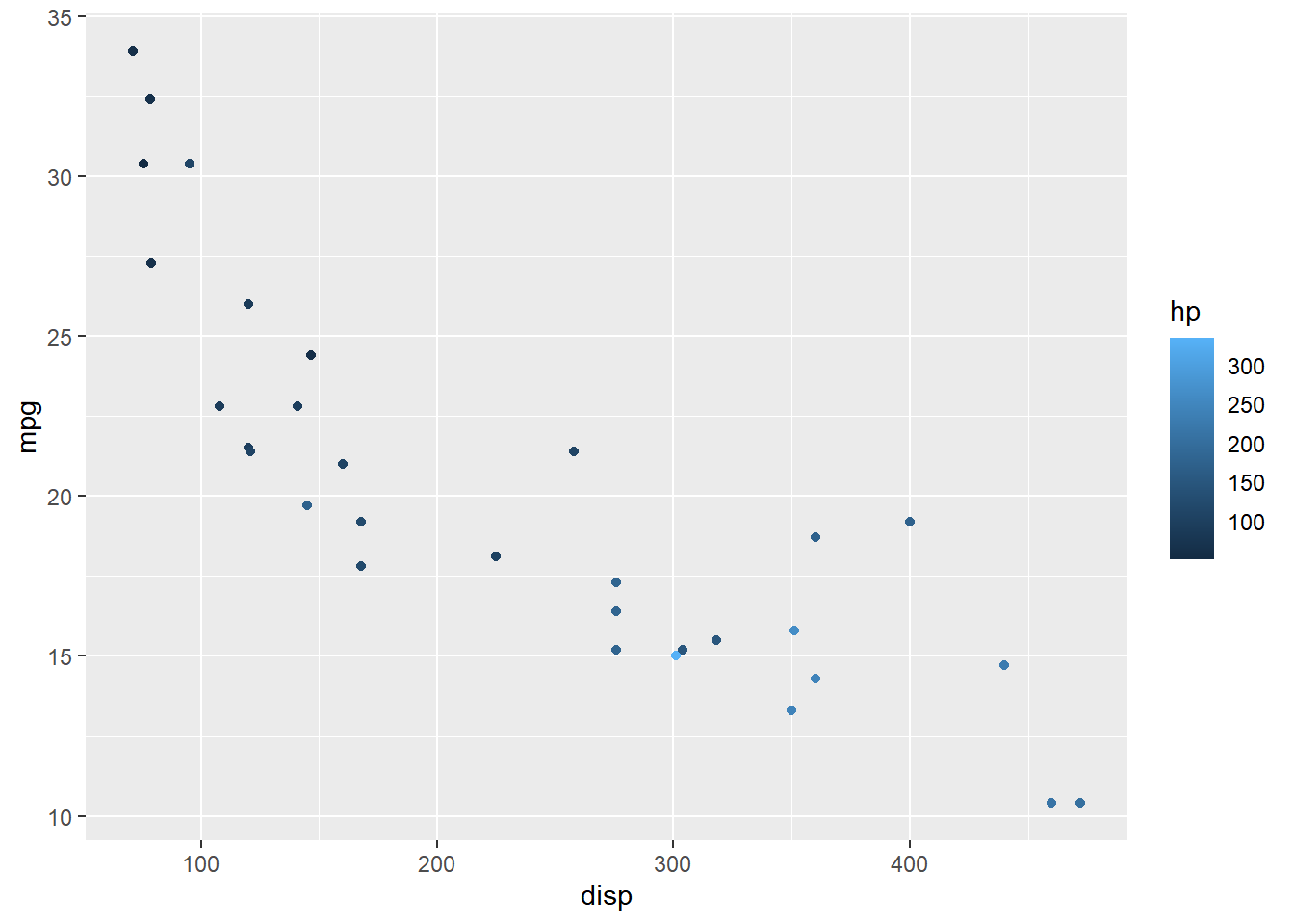
Upper/Lower Limits
The upper and lower limits of the bars can be drawn or undrawn using the
draw.ulim and draw.llim arguments. They both accept logical values.
ggplot(mtcars) +
geom_point(aes(disp, mpg, color = hp)) +
scale_color_continuous(guide = guide_colorbar(
draw.ulim = TRUE, draw.llim = FALSE))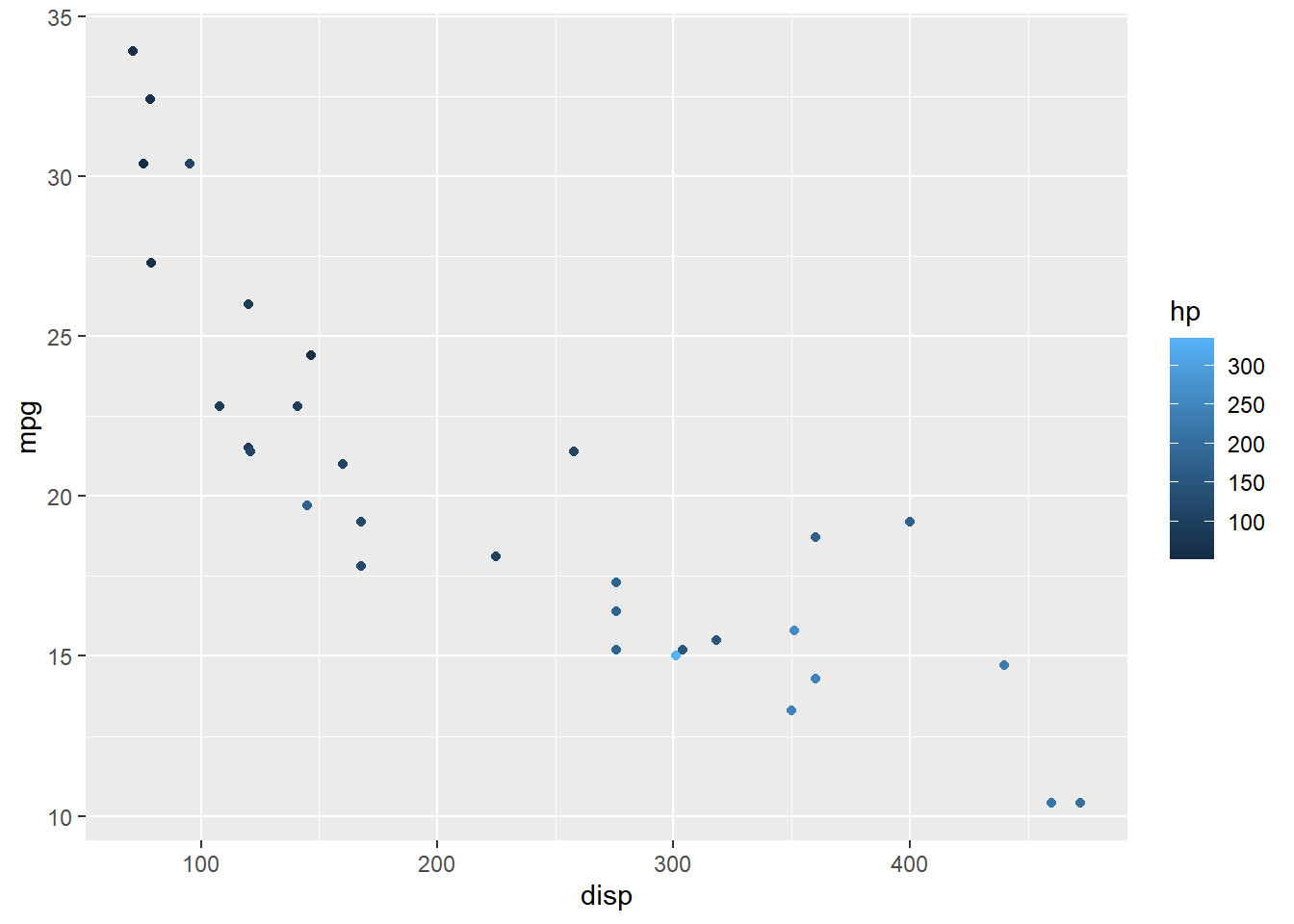
Guides: Color, Shape & Size
The guides() function can be used to create multiple legends to act as a
guide for color, shape, size etc. as shown below. First, we map color,
shape and size to different variables. Next, in the guides() function, we
supply values to each of the above aesthetics to indicate the type of legend.
ggplot(mtcars) +
geom_point(aes(disp, mpg, color = hp,
size = qsec, shape = factor(gear))) +
guides(color = "colorbar", shape = "legend", size = "legend")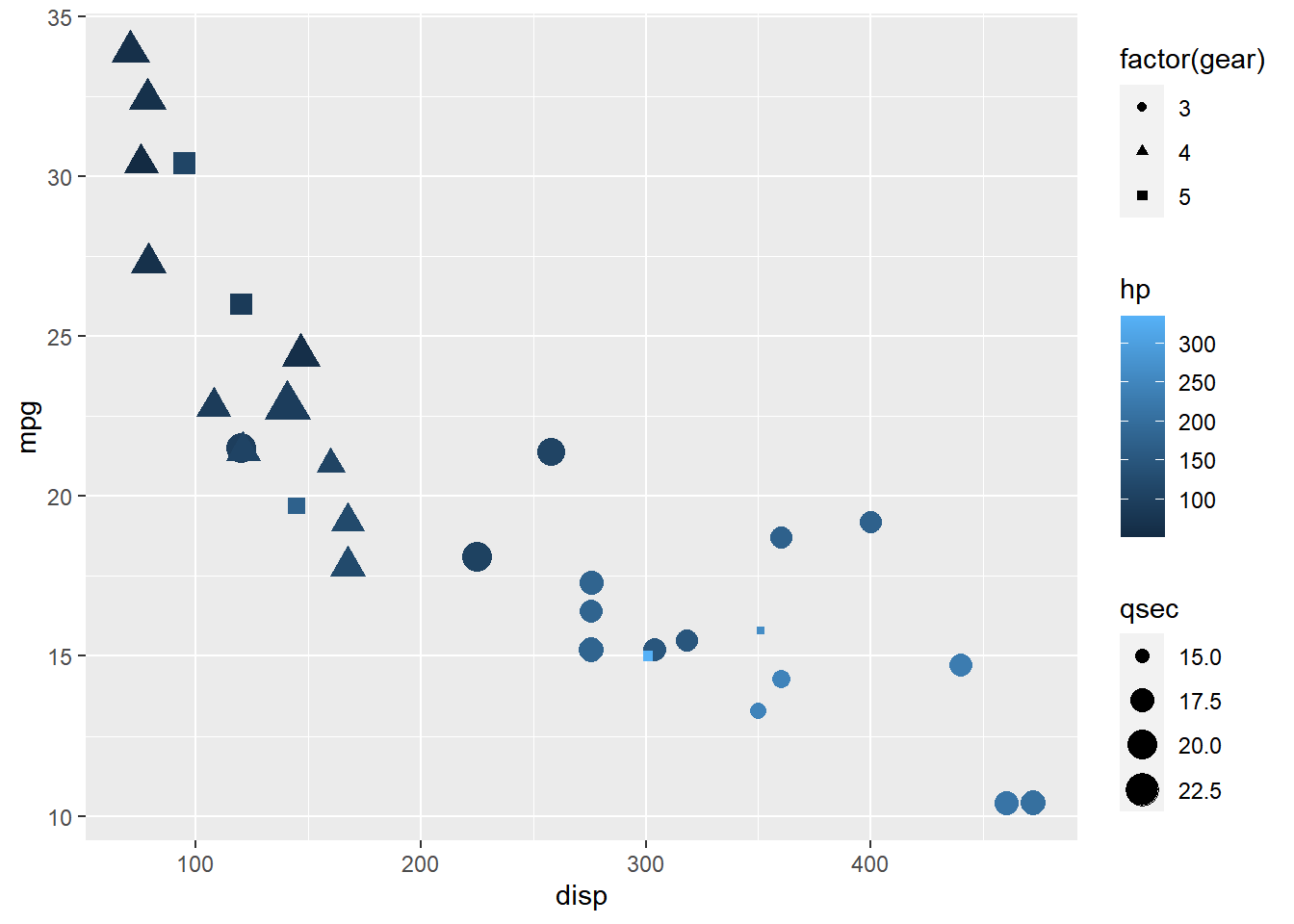
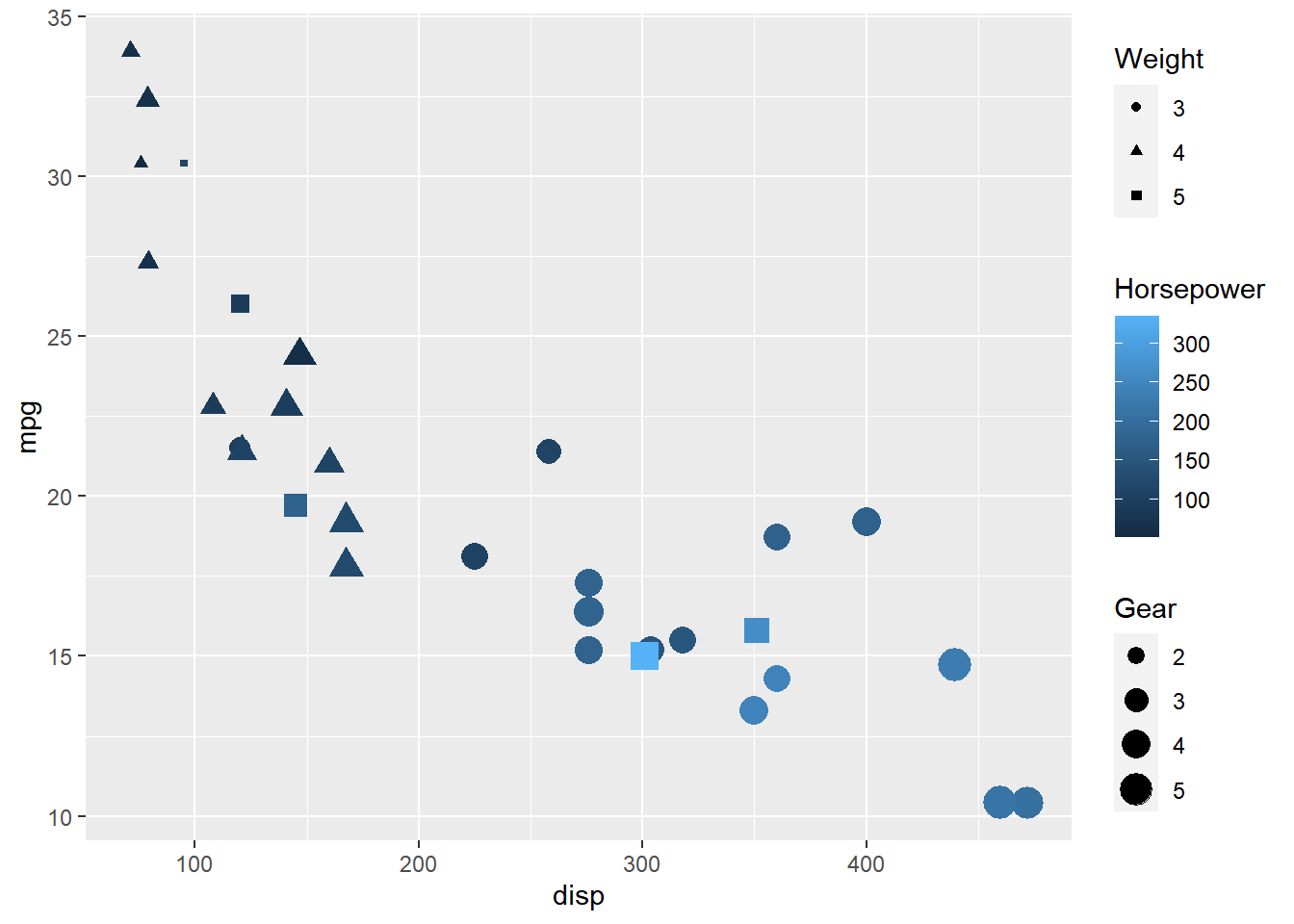
Guides: Title
To modify the components of the different legends, we must use the
guide_* family of functions. In the below example, we use guide_colorbar()
for the legend acting as guide for color mapped to a continuous variable and
guide_legend() for the legends acting as guide for shape/size mapped to
categorical variables.
ggplot(mtcars) +
geom_point(aes(disp, mpg, color = hp, size = wt, shape = factor(gear))) +
guides(color = guide_colorbar(title = "Horsepower"),
shape = guide_legend(title = "Weight"), size = guide_legend(title = "Gear")
)
Summary
In this post, we will learn to modify legend
- title
- label
- and bar
Up Next..
In the next post, we will learn faceting.